What is Ergonomics?
This section will define ergonomics and explain how it applies to the workplace and daily life. It will also highlight some of the key benefits of ergonomic design, such as improved posture, increased comfort, and reduced strain on the body.
The Health Risks of Poor Ergonomics
This section will explore the various health risks associated with poor ergonomics, including musculoskeletal disorders, eye strain, and headaches. It will explain how these conditions can arise from poor posture, repetitive motion, and other factors.
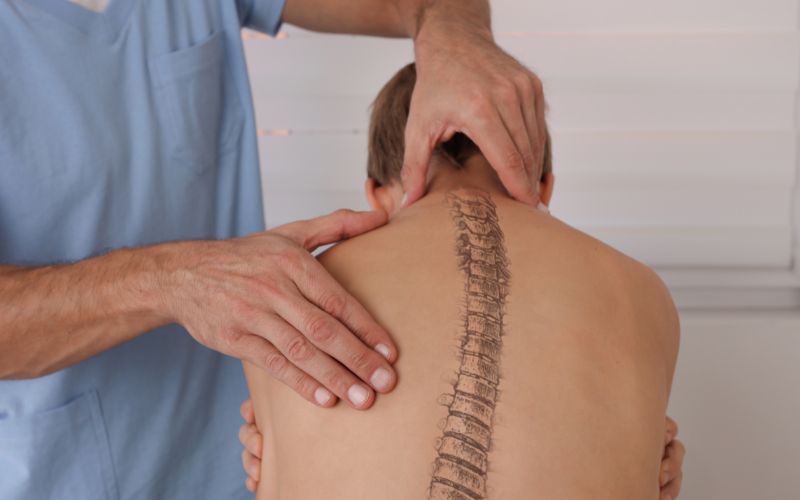
Musculoskeletal Disorders
This subsection will provide an in-depth analysis of musculoskeletal disorders, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, tennis elbow, and tendonitis. It will explain how these conditions arise and how they can be prevented.
Eye Strain
This subsection will explore the causes and symptoms of eye strain, such as blurry vision, headaches, and dry eyes. It will also provide some practical tips for reducing eye strain, such as taking breaks, adjusting lighting, and optimizing screen settings.
Ergonomics in the Workplace
This section will focus on how to implement ergonomic design principles in the workplace. It will explore some common workplace scenarios where ergonomic design is essential, such as office workstations, standing desks, and manual labor jobs.
Office Workstations
This subsection will provide practical tips for setting up an ergonomic workstation, such as proper monitor height, keyboard placement, and chair adjustment. It will also highlight some common mistakes people make when setting up their workstations.
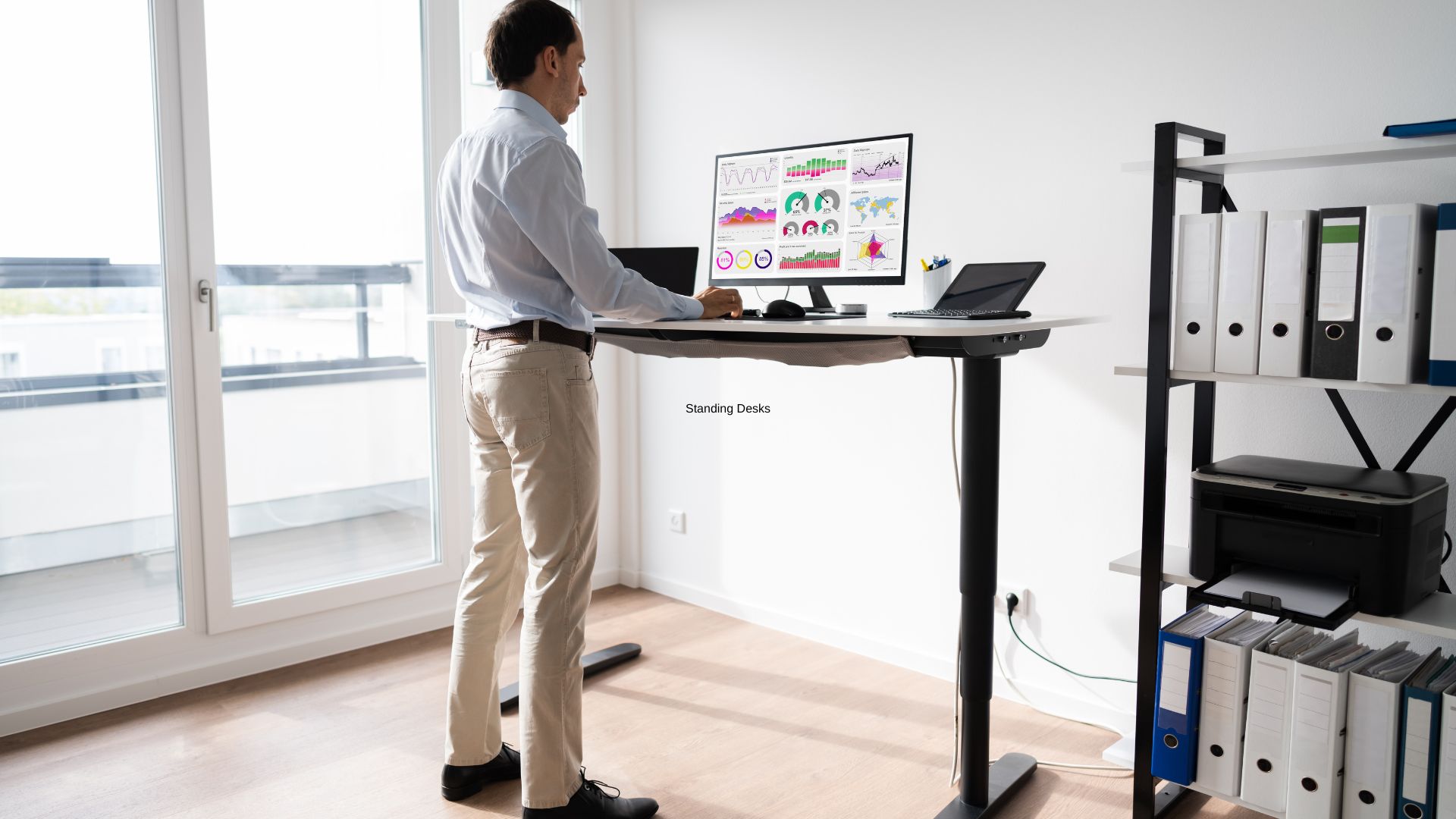
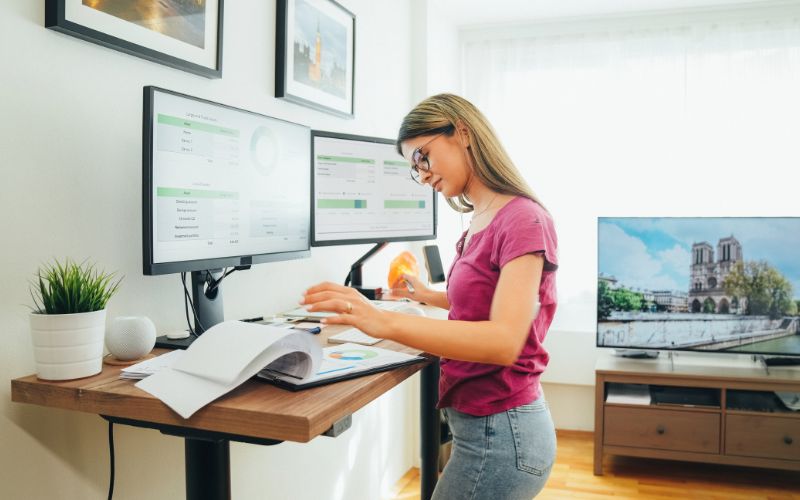
Standing Desks
This subsection will explore the benefits and drawbacks of standing desks and provide some tips for using them properly. It will also address some common misconceptions about standing desks.
Manual Labor Jobs
This subsection will discuss how ergonomic design can improve manual labor jobs, such as manufacturing and construction. It will explore some common ergonomic hazards in these industries, such as heavy lifting, repetitive motion, and awkward postures.
Ergonomics in Daily Life
This section will explore how to apply ergonomic design principles in daily life outside of the workplace. It will highlight some common scenarios where ergonomic design is important, such as driving, sleeping, and exercising.
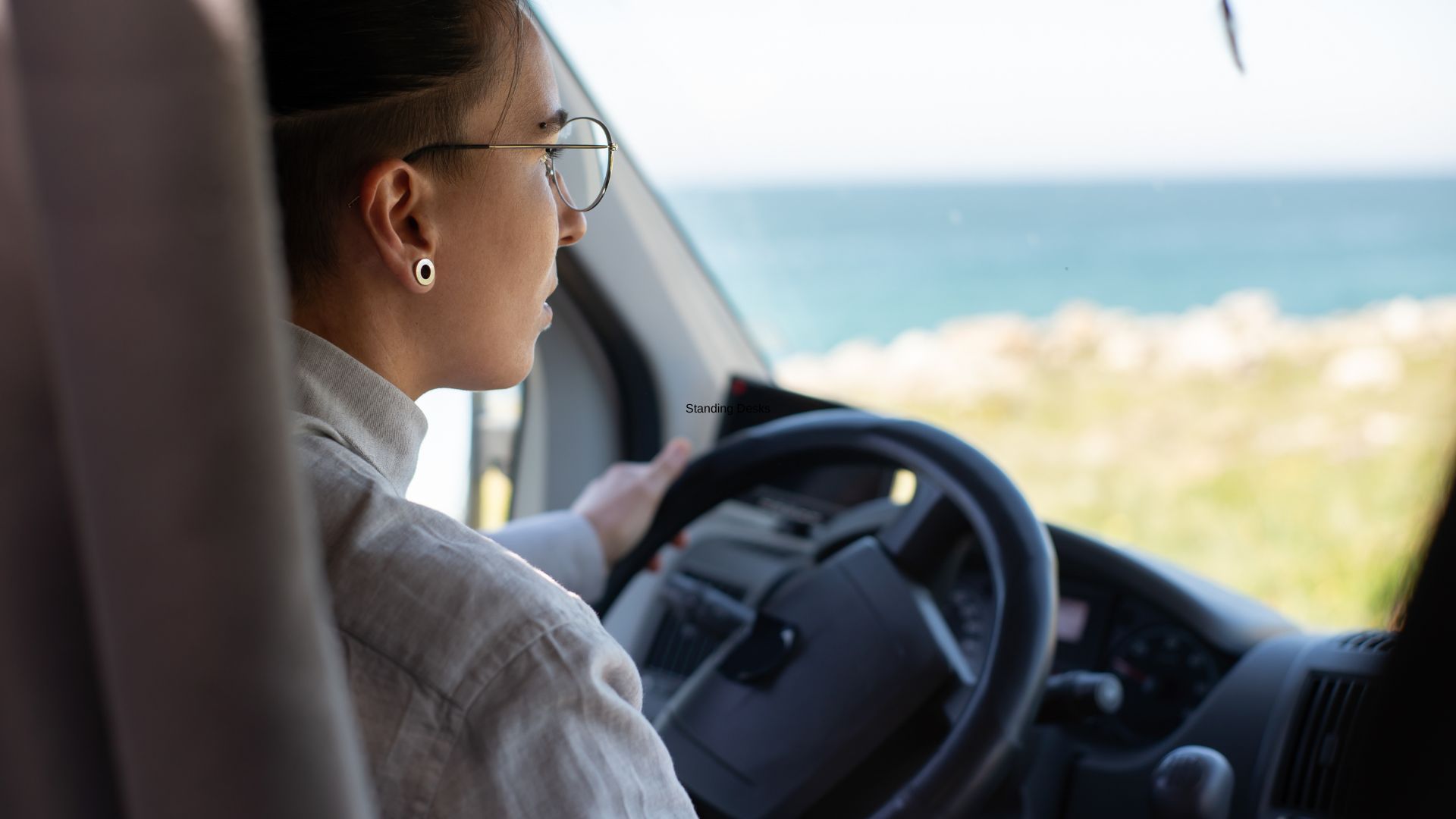
Driving
This subsection will provide some practical tips for maintaining good posture while driving, such as adjusting the seat position and using lumbar support. It will also highlight some common mistakes people make while driving that can lead to poor ergonomics.
Sleeping
This subsection will explore the importance of ergonomic design in sleeping and provide some tips for maintaining good posture while sleeping, such as using the right pillow and mattress. It will also address some common misconceptions about sleep ergonomics.
Exercising
This subsection will discuss how to apply ergonomic design principles while exercising and provide some tips for preventing injuries. It will explore some common ergonomic hazards in exercise, such as overexertion and poor form.
FAQ
Poor ergonomics can lead to various health issues, such as musculoskeletal disorders, eye strain, and headaches. These conditions can arise from poor posture, repetitive motion, and other factors.
Some practical tips for setting up an ergonomic workstation include adjusting the monitor height, keyboard placement, and chair position. It’s also important to take breaks and stretch periodically to avoid repetitive motion injuries.
Standing desks can be harmful to your health if they are not used properly. It’s important to adjust the height of the desk and monitor to maintain good posture, and to alternate between sitting and standing throughout the day.
Ergonomic design principles can be applied to manual labor jobs by identifying and addressing ergonomic hazards, such as heavy lifting, repetitive motion, and awkward postures. This can involve redesigning tools and equipment, implementing proper training, and providing personal protective equipment.