I understand the importance of maintaining a healthy and productive workplace. One of the essential aspects of workplace safety is ergonomics, which is the science of designing and arranging work environments to fit the people who use them. In this ultimate guide, we will discuss the best ergonomic practices for computer users to prevent musculoskeletal disorders and increase overall productivity.
Ergonomic safety tips
Correct Seating Posture
Sitting in one spot for an extended period can result in a myriad of issues like backaches, neck pains, and other health conditions.
As such, it’s imperative to sit in a way that adequately supports your back and cultivates good posture.
Below are some guidelines on how to attain the ideal seating posture:
- Keep your feet flat on the ground or place them on a footrest if necessary.
- Ensure your knees form a 90-degree angle, and your thighs are parallel to the floor.
- Adjust the backrest to support your lower back and maintain an upright posture.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed and your elbows at a 90-degree angle.
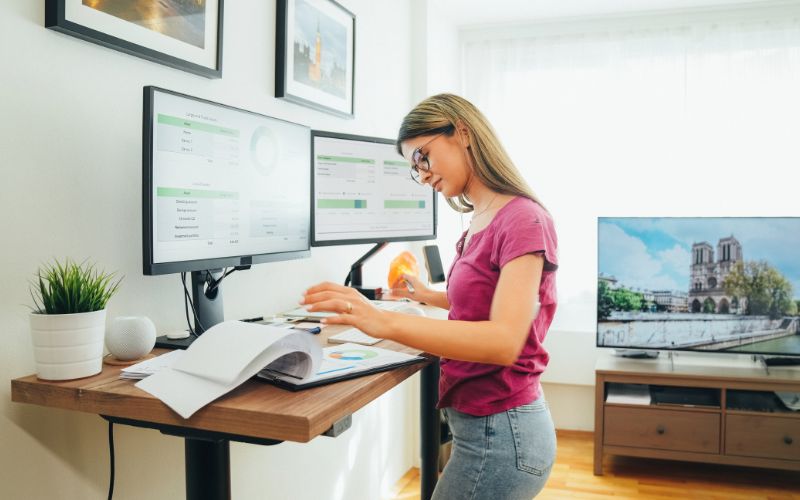
Monitor Placement
Optimal monitor placement can mitigate eye strain and neck pain.
Here are some suggestions to achieve the optimal monitor placement:
- The monitor should be in front of you, with the top of the screen at or slightly below eye level.
- Position the monitor at a comfortable distance, generally an arm’s length away.
- Adjust the brightness and contrast to reduce eye strain.
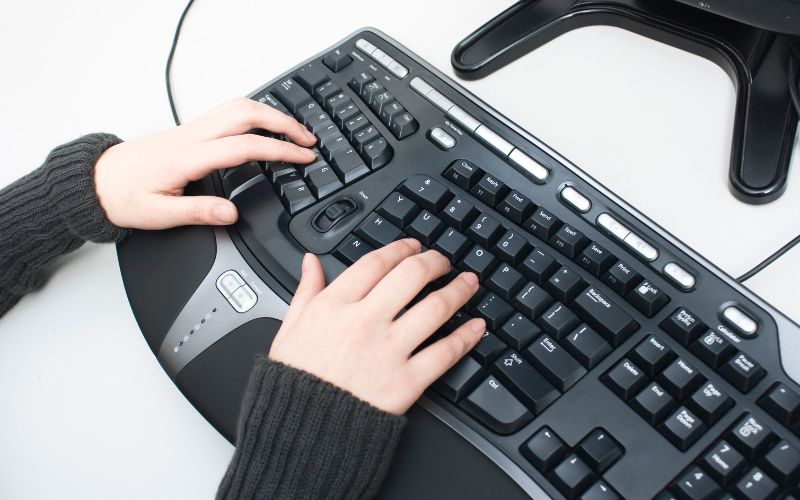
Keyboard and Mouse Placement
Repetitive use of the keyboard and mouse can cause carpal tunnel syndrome and other strain injuries.
Below are some tips to avoid these injuries:
- Ensure the keyboard is at elbow height, with your wrists straight.
- Avoid resting your wrists on the keyboard or desk while typing.
- Place your mouse within easy reach and maintain the same level as your keyboard.
- Use a padded wrist rest to support your wrists during breaks.
Take Frequent Breaks
Taking frequent breaks can prevent eye strain, neck pain, and other health conditions that accompany prolonged sitting.
Here are some tips on how to take breaks:
- Stand up and stretch every 30 minutes.
- Take a five-minute break every hour to rest your eyes and stretch your muscles.
- Walk around or do some light exercises during your break.